Divergence Controls
Front Divergence, Front/Rear Divergence, and Rear Divergence determine the attenuation curves used when positioning sound sources for x-axis front, y-axis front/rear, and x-axis rear. For 3D channel configurations, Height Divergence allows you to determine the attenuation curve when positioning on the z-axis.
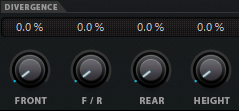
If all divergence controls are set to 0 %, positioning a sound source on a speaker sets all other speakers to level zero. With higher values, the other speakers receive a percentage of the sound source.
Horizontal and vertical lines show the effect of changing the divergence settings:
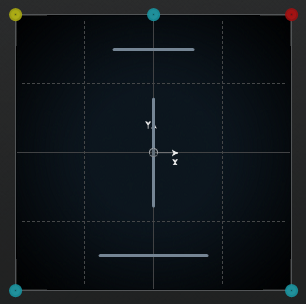
At 0 %, a moving sound source is concentrated in one spot. You can use this to create the impression that something is taking place right in front of the spectator.
At 100 %, a moving sound source is very diffuse and hard to locate. You can use this to create the impression that something is taking place far away from the spectator.
-
Center Distribution and Front Divergence are combined. If the front divergence is set to 100 %, the center distribution has no effect.
-
The setting of the Height Divergence is not shown in the pan areas.